Abstract
Porcine (p) factor (F)VIII has limited cross-reactivity to inhibitors against human (h) FVIII (Lollar P, JBC 1991). Plasma-derived or recombinant pFVIII agents, therefore, have been used as therapeutics for uncontrollable bleedings in congenital or acquired hemophilia A (HA). Alternatively, most of FVIII inhibitors bind to the epitopes located in the A2, C2 and/or A3-C1 domains of FVIII (Scandella D, Blood 1989, Fulcher C, PNAS 1985), and monospecific inhibitors for domains other than A2 and C2 are infrequent (Prescott R, Blood 1997).
In the present study, based on a hypothesis that human-porcine hybrid (hp)FVIII could escape the FVIII-inhibitory effects by inhibitors, we converted A2 domain and/or C2 domain of hFVIII into corresponding sequence of pFVIII, respectively, and investigated the escaping ability of these mutants from inhibitors.
Three mutants were created using stable BHK cell line by converting hFVIII A2 domain and/or C2 domain into corresponding sequence of pFVIII, termed by hp(A2), hp(C2), and hp(A2/C2), respectively. Specific activity assessed by a one-stage clotting assay of hp(A2), hp(C2) and hp(A2/C2) was 0.75, 0.94 and 0.60 relative to hFVIII respectively. First, the escaping ability of these mutants from commercial anti-FVIII A2 or C2 monoclonal antibody (mAb) was investigated. Each of two different anti-hFVIII A2 mAbs and two different anti-C2 mAbs was spiked into FVIII-deficient plasma (FVIIId), respectively at the Bethesda titer of 2.7-4.4 BU/mL, followed by spiking hFVIII or hpFVIII at the concentration of 1 nM each. Incubation of each sample at 37 °C was initiated and FVIII activity was determined (FVIII:C) sequentially, calculating the FVIII:C at the fold of initial (no addition of inhibitor). In anti-A2 mAbs, FVIII:C of hFVIII and hp(C2) were immediately attenuated, resulting in suppression under 20% of initial level after 30 min, however, hp(A2) and hp(A2/C2) were not suppressed at all. In contrast, with anti-C2 mAbs, FVIII:C in hFVIII and hp(A2) was attenuated, whilst hp(C2) and hp(A2/C2) maintained their FVIII:C.
Next, similar experiment was conducted with the purified IgG from the HA patients with inhibitor whose inhibitor was confirmed to recognize A2 only or both A2/C2 domains by Western blotting. Four patients with anti-A2 and anti-A2/C2 inhibitors (2 patients each) were investigated. Mutants converted certain domain(s) could escape inhibitory effect of purified IgG recognizing the corresponding domain(s), although partial attenuation exhibited even in the corresponding mutants.
To further investigation, thrombin generation assay (TGA) and rotation thromboelastometry (ROTEM) were used. In TGA, purified IgG from patient with anti-A2 or anti-A2/C2 inhibitor was added to FVIIId, followed by spiking hFVIII or hpFVIII at the concentration of 1 nM. In the absence of IgG, peak thrombin of FVIIId was 128.0 nM, and then by adding hFVIII, hp(A2), hp(C2) and hp(A2/C2), the parameter enhanced to 228.8, 208.6, 207.3, and 219.9 nM, respectively. In the presence of anti-A2 inhibitor (5.0 BU/mL), peak thrombin of hp(A2) and hp(A2/C2) was not attenuated (203.1 and 257.1 nM), whilst those of hFVIII and hp(C2) was suppressed equally to FVIIId (137.3 and 134.5 nM respectively). As for anti-A2/C2 inhibitor (2.8 BU/mL), only hp(A2/C2) was not attenuated, whereas the others were suppressed comparable to FVIIId .
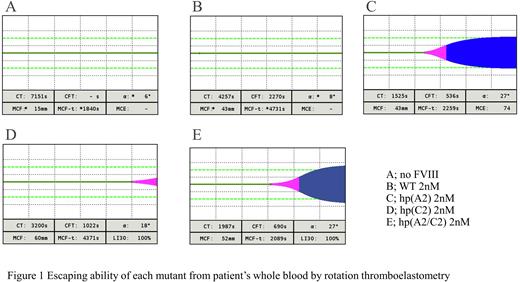
Whole bloods collected from severe HA with anti-A2 inhibitor (3.1 BU/mL) were mixed with hFVIII or hpFVIII at the concentration of 2 nM, respectively, and were measured by ROTEM. Without any FVIII spiking, clot time (CT) was 7,151 sec and clot formation time (CFT) was undetectable. The addition of hp(A2) and hp(A2/C2) shortened CT/CFT to 1,525/536 sec and 1,987/690 sec, respectively, whilst hFVIII or hp(C2) was not effective (4,257/2,270 and 3,200/1,022 sec, respectively). On the other hand, purified IgG from patients with anti-A2/C2 inhibitor was added to whole blood from another severe HA without inhibitor. Under this condition (4.7 BU/mL), only hp(A2/C2) addition shortened CT/CFT from 6,482/2,163 to 1,724/503 sec, whereas the addition of the other FVIII resulted in limited effect to CT/CFT (2,703-4,796/551-2,024).
We concluded that hybrid FVIII converted into porcine A2 and/or C2 domain sequences were able to escape corresponding inhibitors and that hpFVIII could be effective therapeutically for HA patients with inhibitors.
Disclosures
Nakajima:Takeda Pharmaceutical company: Research Funding. Ogiwara:Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Research Funding. Shima:Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; CSL Behring: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.: Speakers Bureau; Novo Nordisk: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Bayer Yakuhin: Honoraria; Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Fujimoto Seiyaku: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Ono Yakuhin: Speakers Bureau; Nara Medical University: Current Employment; UniQure: Consultancy. Nogami:Chugai, Sanofi, Takeda, Bayer, Novo Nordisk, KMBio, CSL Behring, Fujimoto Seiyaku, Sekisui Medical, Sysmex, AsahiKasei: Research Funding; Chugai, Sanofi, Takeda, Bayer, Novo Nordisk, CSL Behring, KMBio, Fujimoto Seiyaku, Sekisu Medical, Sysmex,: Honoraria; Chugai: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal